How it Works
ARTAI presents a simulation environment to impart transparency and enable oversight of recommender algorithms. The approach can be used as an effective way to evaluate algorithms for potential risk within a controlled environment.
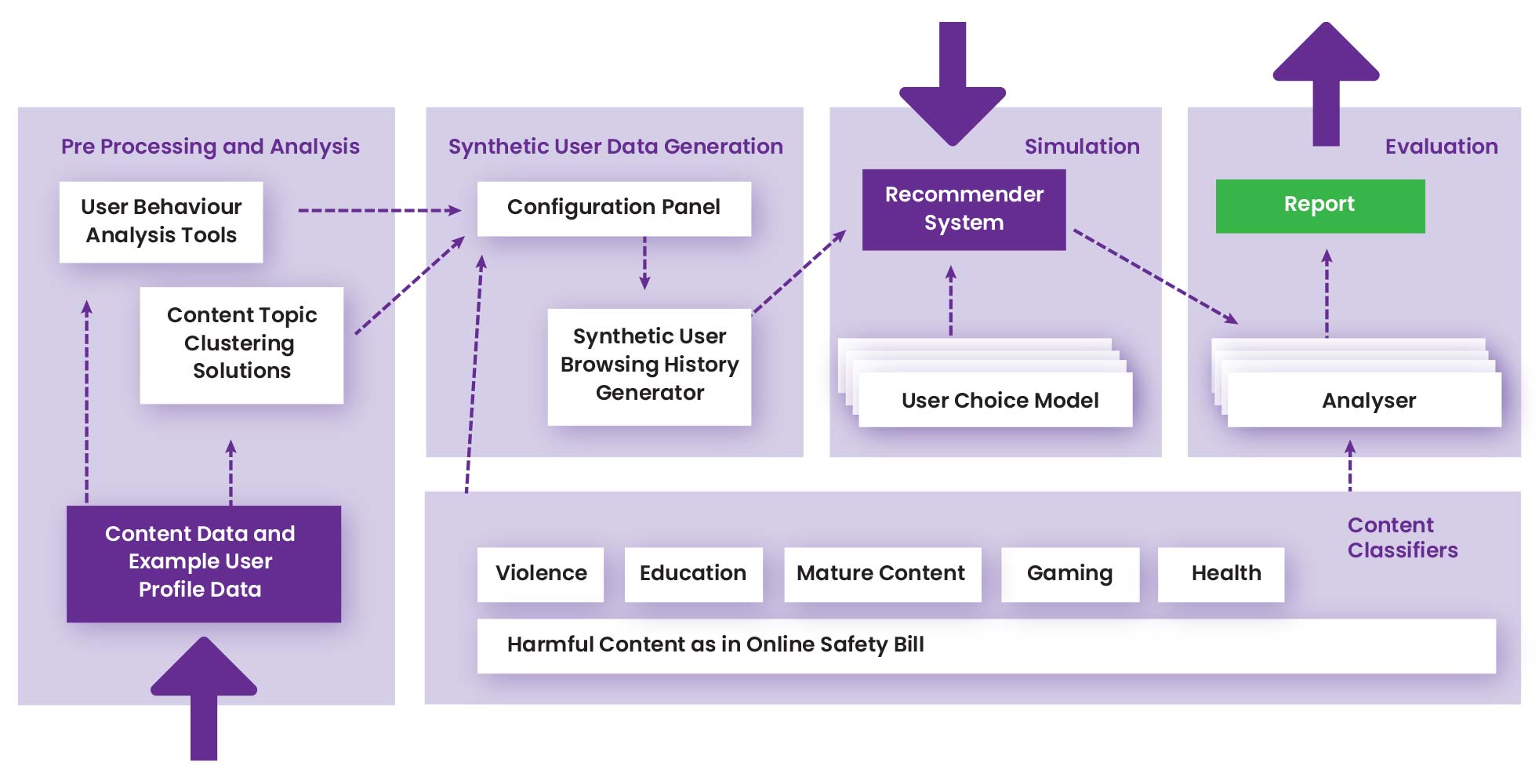
The ARTAI environment simulates the interaction between users and recommendation algorithms. The interface enables setting up of experiments and presents an easily interpretable visualisation of results. The simulation environment enables replication of feedback loops where a recommendation algorithm recommends a set of items from a much larger set based on a user’s profile. These items are then passed into the user choice model. The user choice model simulates how users select items from the set of items recommended to them. Finally, these selected articles are added to the user’s profile to complete the recommendation process. The simulation environment repeatedly executes the recommendation feedback loop to analyse the evolution of user engagement and content consumption patterns.
ARTAI system architecture
Pre-Processing and Analysis
The simulation framework initially utilised a recently released large-scale dataset of short videos MicroLens (Ni et al., 2023) and a news article dataset for recommendations (Wu et al., 2020). These datasets include extensive user-item interaction data along with visual and textual information such as the original video content, comments and titles. In future further datasets will be added and users may upload and annotate their own.
User Profiles and Behaviour Models
Sample user profiles can be set up in the user interface by setting the interest profile of users. This component draws on user history data available in the micro-lens dataset and plans are in place to enable synthetic user data generation. These user profiles can be set up to reflect real-world scenarios based on testimony from users of online platforms and research on social risks of online platforms.
The developed simulation framework provides a variety of user choice models, such as Equal-Rec, Top-K-Rec etc (Ruan et al., 2024). These user choice strategies are used to model how users interact with recommender systems and how much the content they view is influenced by what is recommended to them.
Content Classifiers
The content classification categories implemented and available in the ARTAI prototype are a combination of pre-annotated categories in the microlens dataset along with categories resulting from evaluation of the videos using NLP techniques.
Recommender Algorithms
The simulation framework supports recommender algorithms including such as NexItNet, GRU4Rec and SASRec regarding video recommendations (Yuanet al., 2019; Hidasi et al., 2015; Kang et al., 2018). The future development plan is that new recommender algorithms may be added and the platform can be integrated in industry settings through the development of an API.
Risk Evaluation
We implemented an evaluation component to enable visualisation and analysis of how different kinds of users are recommended content over time in a way that is interpretable to those who are not experts in recommender algorithms.
The results include: 1. Visualisation results of video classification. 2. Preference distribution of user groups. 3.
Long-term observation results in preference distribution of different user groups under different user choice strategies and recommendation algorithms.